TKI-AMC
 Detecting blood closts causing stroke with AI as early as possible
Detecting blood closts causing stroke with AI as early as possible
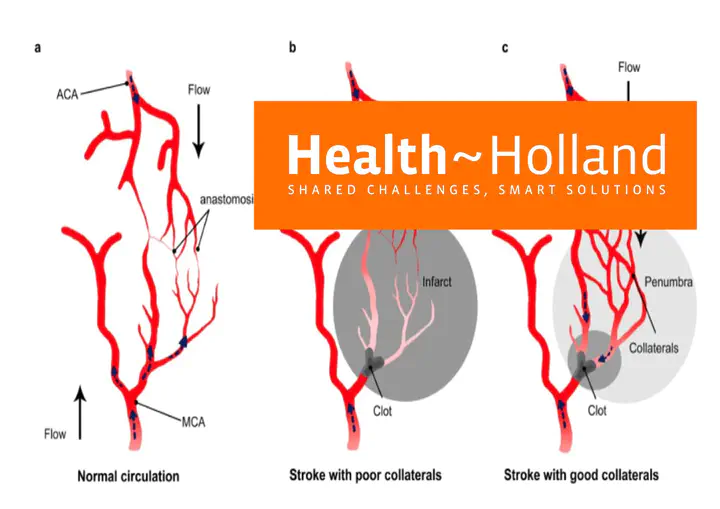
Stroke is the leading cause of disability in adults and every year 40,000 patients suffer stroke in the Netherlands. Large vessel occlusions (LVO) disproportionally contribute to stroke-related dependence and death. After publication of the Dutch MR CLEAN trial in 2015, endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) has been described as one of the biggest breakthroughs in modern medicine. EVT for ischemic stroke patients with LVO arriving within 6 hours increases the odds of achieving a good outcome nearly 2.5 fold. Imaging based treatment selection promises equal effectiveness of EVT for LVO stroke in patients arriving later or for wake-up strokes and requires information on the volume of salvageable and infarcted tissue.
Assessment of salvageable and infarcted tissue with CT perfusion (CTP) is possible but difficult. Most primary stroke centres (PSCs) cannot perform and interpret CTP necessitating transfer from PSCs to comprehensive stroke centres (CSCs). Conversely, non-contrast CT (NCCT) and CT angiography (CTA) are currently available in all PSCs.
The aim of AIRBORNE is to develop AI-based tooling for estimation of infarct volume on NCCT and CTA scans using deep learning neural networks making CTP unnecessary. Early treatment selection will speed up transfers and decrease onset to treatment times, improving the outcome of treated patients This project contributes to topsector Life Sciences & Health goals by applying AI algorithms in cloud-based decision tools to improve outcomes and healthcare efficacy while gaining insight into data efficient AI.